CurveOfGrowth¶
- class photutils.profiles.CurveOfGrowth(data, xycen, radii, *, error=None, mask=None, method='exact', subpixels=5)[source]¶
Bases:
ProfileBaseClass to create a curve of growth using concentric circular apertures.
The curve of growth profile represents the circular aperture flux as a function of circular radius.
- Parameters:
- data2D
numpy.ndarray The 2D data array. The data should be background-subtracted. Non-finite values (e.g., NaN or inf) in the
dataorerrorarray are automatically masked.- xycentuple of 2 floats
The
(x, y)pixel coordinate of the source center.- radii1D float
numpy.ndarray An array of the circular radii.
radiimust be strictly increasing with a minimum value greater than zero, and contain at least 2 values. The radial spacing does not need to be constant.- error2D
numpy.ndarray, optional The 1-sigma errors of the input
data.erroris assumed to include all sources of error, including the Poisson error of the sources (seecalc_total_error) .errormust have the same shape as the inputdata. Non-finite values (e.g., NaN or inf) in thedataorerrorarray are automatically masked.- mask2D bool
numpy.ndarray, optional A boolean mask with the same shape as
datawhere aTruevalue indicates the corresponding element ofdatais masked. Masked data are excluded from all calculations.- method{‘exact’, ‘center’, ‘subpixel’}, optional
The method used to determine the overlap of the aperture on the pixel grid:
'exact'(default): The the exact fractional overlap of the aperture and each pixel is calculated. The aperture weights will contain values between 0 and 1.'center': A pixel is considered to be entirely in or out of the aperture depending on whether its center is in or out of the aperture. The aperture weights will contain values only of 0 (out) and 1 (in).'subpixel': A pixel is divided into subpixels (see thesubpixelskeyword), each of which are considered to be entirely in or out of the aperture depending on whether its center is in or out of the aperture. Ifsubpixels=1, this method is equivalent to'center'. The aperture weights will contain values between 0 and 1.
- subpixelsint, optional
For the
'subpixel'method, resample pixels by this factor in each dimension. That is, each pixel is divided intosubpixels**2subpixels. This keyword is ignored unlessmethod='subpixel'.
- data2D
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from astropy.modeling.models import Gaussian2D >>> from astropy.visualization import simple_norm >>> from photutils.centroids import centroid_quadratic >>> from photutils.datasets import make_noise_image >>> from photutils.profiles import CurveOfGrowth
Create an artificial single source. Note that this image does not have any background.
>>> gmodel = Gaussian2D(42.1, 47.8, 52.4, 4.7, 4.7, 0) >>> yy, xx = np.mgrid[0:100, 0:100] >>> data = gmodel(xx, yy) >>> error = make_noise_image(data.shape, mean=0., stddev=2.4, seed=123) >>> data += error
Create the curve of growth.
>>> xycen = centroid_quadratic(data, xpeak=48, ypeak=52) >>> radii = np.arange(1, 26) >>> cog = CurveOfGrowth(data, xycen, radii, error=error, mask=None)
>>> print(cog.radius) [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25]
>>> print(cog.profile) [ 130.57472018 501.34744442 1066.59182074 1760.50163608 2502.13955554 3218.50667597 3892.81448231 4455.36403436 4869.66609313 5201.99745378 5429.02043984 5567.28370644 5659.24831854 5695.06577065 5783.46217755 5824.01080702 5825.59003768 5818.22316662 5866.52307412 5896.96917375 5948.92254787 5968.30540534 5931.15611704 5941.94457249 5942.06535486]
>>> print(cog.profile_error) [ 5.32777186 9.37111012 13.41750992 16.62928904 21.7350922 25.39862532 30.3867526 34.11478867 39.28263973 43.96047829 48.11931395 52.00967328 55.7471834 60.48824739 64.81392778 68.71042311 72.71899201 76.54959872 81.33806741 85.98568713 91.34841248 95.5173253 99.22190499 102.51980185 106.83601366]
Plot the curve of growth.
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf,svg)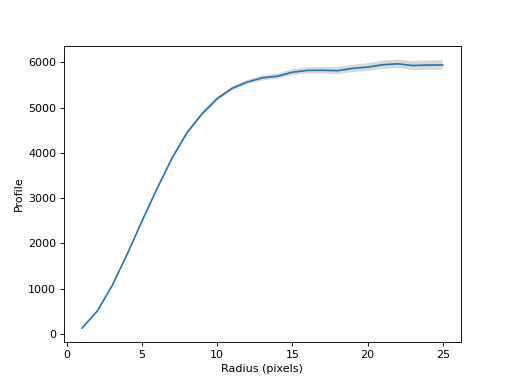
Normalize the profile and plot the normalized curve of growth.
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf,svg)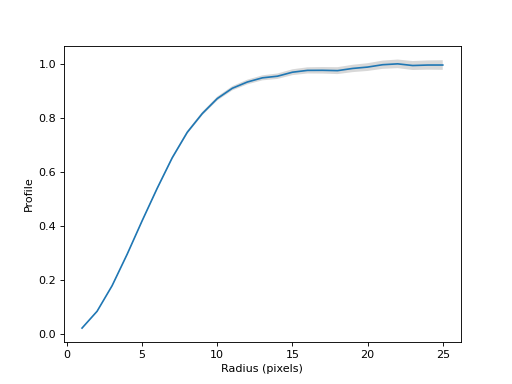
Plot a couple of the apertures on the data.
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf,svg)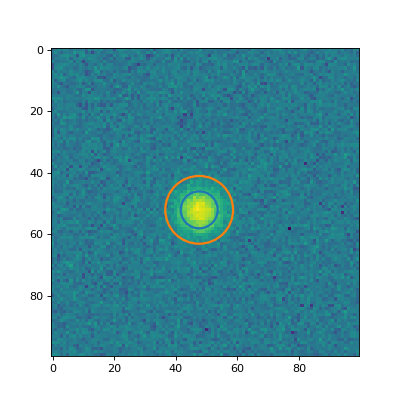
Attributes Summary
A list of
CircularApertureobjects used to measure the profile.The unmasked area in each circular aperture as a function of radius as a 1D
ndarray.The curve-of-growth profile as a 1D
ndarray.The curve-of-growth profile errors as a 1D
ndarray.The profile radius in pixels as a 1D
ndarray.Methods Summary
normalize([method])Normalize the profile.
plot([ax])Plot the profile.
plot_error([ax])Plot the profile errors.
Attributes Documentation
- apertures¶
A list of
CircularApertureobjects used to measure the profile.If
radius_minis zero, then the first item will beNone.
Methods Documentation
- normalize(method='max')¶
Normalize the profile.
- Parameters:
- method{‘max’, ‘sum’}, optional
The method used to normalize the profile:
‘max’ (default): The profile is normalized such that its peak value is 1.
‘sum’: The profile is normalized such that its sum (integral) is 1.
- plot(ax=None, **kwargs)¶
Plot the profile.
- Parameters:
- ax
matplotlib.axes.AxesorNone, optional The matplotlib axes on which to plot. If
None, then the currentAxesinstance is used.- **kwargs
dict Any keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.plot.
- ax
- Returns:
- lineslist of
Line2D A list of lines representing the plotted data.
- lineslist of
- plot_error(ax=None, **kwargs)¶
Plot the profile errors.
- Parameters:
- ax
matplotlib.axes.AxesorNone, optional The matplotlib axes on which to plot. If
None, then the currentAxesinstance is used.- **kwargs
dict Any keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.fill_between.
- ax
- Returns:
- lines
matplotlib.collections.PolyCollection A
PolyCollectioncontaining the plotted polygons.
- lines